'Once in a millennium': Record-breaking rogue wave measured off Vancouver Island
A massive ocean wave that was tracked off the west coast of Vancouver Island in 2020 is now considered the most extreme rogue wave ever recorded, according to scientists at the University of Victoria.
At 17.6 metres tall, the rogue swell reached as high as a four-storey building when it was detected near Ucluelet, B.C., in November 2020.
The wave is the subject of a new research paper published last week in the journal Scientific Reports by UVic scientists Johannes Gemmrich and Leah Cicon.
Also known as freak waves or killer waves, rogue waves are defined as one-off waves that reach at least twice as high as the surrounding ocean swell. Their tendency to occur with great force and little warning makes them especially dangerous for seafarers.
Scientists have been attempting to measure rogue waves since 1995, when the first such wave was recorded off Norway at a height of 25.6 metres.
Known as the "Draupner wave," it was spotted amid 12-metre seas, placing it at just over double the height of the surrounding waters.
'ONCE IN 1,300 YEARS'
While the Draupner wave was taller than the rogue wave measured off Ucluelet, the Ucluelet wave was nearly triple the height of the surrounding six-metre swells, and was therefore more "rogue" than its predecessor.
"Proportionally, the Ucluelet wave is likely the most extreme rogue wave ever recorded," said Gemmrich, who studies large waves off the B.C. coast as part of his work as a research physicist.
"Only a few rogue waves in high sea states have been observed directly, and nothing of this magnitude," he said. "The probability of such an event occurring is once in 1,300 years."
The wave was recorded by a sensor buoy deployed by MarineLabs Data Systems at Amphitrite Bank, approximately seven kilometres from the Ucluelet shoreline in water 45 metres deep.
The wave was the fourth crest in a group of 10 much smaller waves. "This is consistent with the fact that rogue waves generally occur near the centre of a group and are unexpected, i.e. there is not a gradual build-up of individual wave heights," the study authors wrote.
"The unpredictability of rogue waves, and the sheer power of these 'walls of water' can make them incredibly dangerous to marine operations and the public," said MarineLabs CEO Scott Beatty.
"The potential of predicting rogue waves remains an open question, but our data is helping to better understand when, where and how rogue waves form, and the risks that they pose," Beatty added.
The observation of the Draupner wave on Jan. 1, 1995, proved to scientists that rogue waves are more than seafarer folklore, the UVic researchers said. "Only a few rogue waves in high sea states have been observed directly, but they can pose a danger to marine operations, onshore and offshore structures, and beachgoers."
Beatty, the MarineLabs CEO, added that "capturing this once-in-a-millennium wave, right in our backyard, is a thrilling indicator of the power of coastal intelligence to transform marine safety."
CTVNews.ca Top Stories

Canada Disability Benefit needs to safeguarded from clawbacks, MPs unanimously agree
The federal government needs to safeguard the incoming Canada Disability Benefit from clawbacks and do more to ensure it actually meets the stated aim of lifting people living with disabilities out of poverty, MPs from all parties agree.
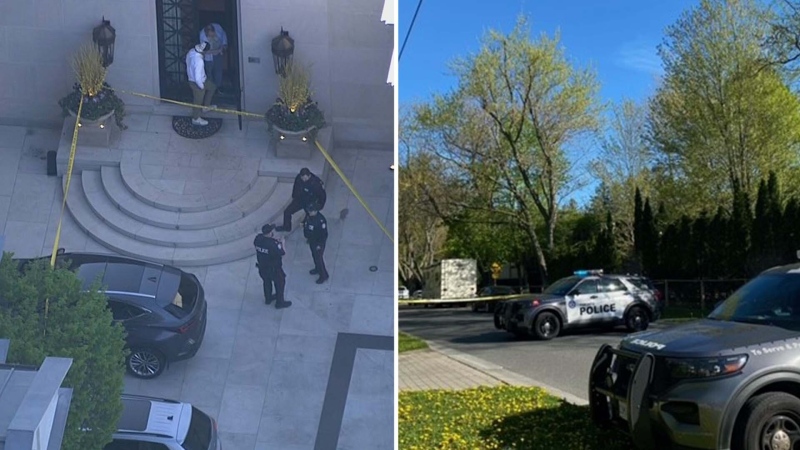
BREAKING Security guard shot, seriously injured outside of Drake's Toronto mansion
A security guard working at Drake’s Bridle Path mansion in Toronto was seriously injured in a shooting outside the residence early Tuesday morning, police said.
King Charles too busy to see son Prince Harry during UK trip
Prince Harry will not be seeing his father King Charles during his current visit to Britain as the monarch will be too busy, Harry's spokesperson said on Tuesday.
opinion Tom Mulcair: Turfing Poilievre from House a clear sign of desperation by Trudeau Liberals
When Speaker Greg Fergus tossed out Pierre Poilievre from the House last week, "those of us who have experience as parliamentarians simply couldn't believe our eyes," writes former NDP leader Tom Mulcair in his column for CTVNews.ca
Your body needs these three forms of movement every week
Movement is movement, right? Not exactly. Here’s what your body is looking for in addition to your morning walk or yoga session, according to experts.
Six Canadian children repatriated from detention in Syria, Global Affairs Canada says
The Global Affairs Department says six Canadian children have been repatriated from detention in northeastern Syria.
'It looked so legit': Ontario man pays $7,700 for luxury villa found on Booking.com, but the listing was fake
An Ontario man says he paid more than $7,700 for a luxury villa he found on a popular travel website -- but the listing was fake.
Quebec to limit sperm donations per donor after 3 men from same family father hundreds of children
Quebec is looking at tightening the regulations around sperm donation in the province following the release of a documentary that revealed three men from the same family fathered hundreds of children.
Canadian cadets rock mullets and place second at U.S. military competition
Sporting mullets, Canadian Armed Forces officer cadets placed second in an annual military skills competition in the U.S.