Vancouver Island marmots released onto Mount Washington
The number of Vancouver Island marmots in the wild increased this week, with 10 of the critically endangered rodents released onto a Mount Washington ski run.
The Marmot Recovery Foundation, which breeds the animals in captivity in hopes of restoring the wild population, released six marmots on Tuesday and four more Wednesday morning.
"The idea right now is to get these marmots who have never been out in the wild before their first taste of life in the wild," said Adam Taylor, the foundation's executive director.
"Some of them will stay resident here and some of them will be trapped again next year and be moved to more remote locations in Strathcona Provincial Park."
In all, the foundation plans to release 25 of the captive-bred animals in 2022. Those plans have been made complicated by the colder-than-average spring, which has left snow on much of the terrain where the marmots typically live.
"There's some concern that this snow is burying the vegetation that these marmots that are emerging from hibernation," said Taylor. "That's what they rely on to eat."
The foundation has been supplementing the animals' food sources, and acknowledges that the marmots themselves have been a food source for hungry cougars.
"It's pretty deeply frustrating to be entirely honest," Taylor said. "Marmots are prey species. We know they're going to be eaten. We put a lot of sweat equity and heart equity into each one of these animals."
Vancouver Island University biology professor Jamie Gorrell has been studying the marmots with his team for the last few years. They've been working to compare the size of habitat required by wild-born marmots to that required by those bred in captivity.
He said the technique the team uses will likely be applicable to research on other species as well.
"We take a GPS location of where they are and then we combine GPS location data from the whole season to create an area map to see how much space the marmots use, or how much they move around over the season," Gorrell explained.
Initial results suggest that the marmots born in captivity require more space than those born in the wild.
"I guess it sort of implies that the marmots need time to get their bearings when they get put in a new location," Gorrell said. "They need to sort of survey the landscape to find out where they want to go."
With files from CTV News Vancouver Island's Gord Kurbis
CTVNews.ca Top Stories
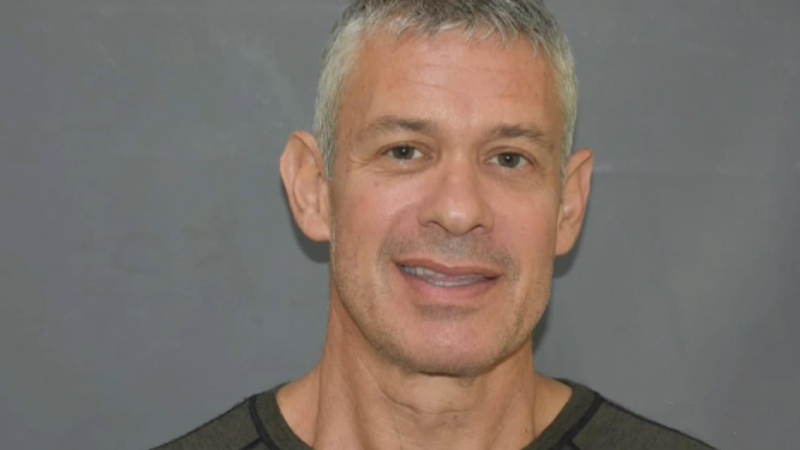

American millionaire Jonathan Lehrer denied bail after being charged with killing Canadian couple
American millionaire Jonathan Lehrer, one of two men charged in the killings of a Canadian couple in Dominica, has been denied bail.
LeBlanc says he plans to run in next election, under Trudeau's leadership
Cabinet minister Dominic LeBlanc says he plans to run in the next election as a candidate under Prime Minister Justin Trudeau's leadership, amid questions about his rumoured interest in succeeding his longtime friend for the top job.
Sports columnist apologizes for 'oafish' comments directed at Caitlin Clark. The controversy isn't over
A male columnist has apologized for a cringeworthy moment during former University of Iowa superstar and college basketball's highest scorer Caitlin Clark's first news conference as an Indiana Fever player.
U.S. vetoes a widely supported UN resolution backing full membership for Palestine
The United States has vetoed a widely backed UN resolution that would have paved the way for full United Nations membership for the state of Palestine.
Grandparent scam suspects had ties to Italian organized crime, police allege
A group of suspects that allegedly defrauded seniors across Ontario and other parts of Canada using a so-called emergency grandparent scam appear to have ties to 'Italian traditional organized crime,' according to an investigator involved in the OPP-led probe.
Health Canada to change sperm donor screening rules for men who have sex with men
Health Canada will change its longstanding policy restricting gay and bisexual men from donating to sperm banks in Canada, CTV News has learned. The federal health agency has adopted a revised directive removing the ban on gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men, effective May 8.
Prince Harry formally confirms he is now a U.S. resident
Prince Harry, the son of King Charles III and fifth in line to the British throne, has formally confirmed he is now a U.S. resident.
Cat found on Toronto Pearson airport runway 3 days after going missing
Kevin the cat has been reunited with his family after enduring a harrowing three-day ordeal while lost at Toronto Pearson International Airport earlier this week.
'Shopaholic' author Sophie Kinsella reveals brain cancer diagnosis
Sophie Kinsella, the best-selling author behind the 'Shopaholic' book series, has revealed that she is receiving treatment for brain cancer.